Written by Dr Ambi Sud
If you’re struggling with acne, dark spots, melasma, rosacea, or uneven skin tone and texture, you’re not alone. Many people search for the best treatments for hyperpigmentation, clogged pores, and redness, and Azelaic Acid (AzA) and Potassium Azeloyl Diglycinate (PAD) are two powerful ingredients that can be combined with others in Qr8’s customised formulations to target your individual skin concerns.
Known individually for their ability to help clear breakouts, improve congested pores, reduce acne scars, fade pigmentation, or improve skin tone and redness, these ingredients can be combined into formulations to combat inflammation and rosacea papules and pustules while brightening and smoothing the skin.
But what exactly are AzA and PAD, and how do they work? Qr8’s Clinical Lead, Dr Ambi Sud, breaks it down for you.
What Is Azelaic Acid? The Dermatologist-Approved Ingredient for Acne, Pigmentation & Clearer Skin
Azelaic acid, Aza, (chemical name: 1,7-heptanedicarboxylic acid) is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid found in grains like wheat, rye, and barley. For dermatological formulations, it is laboratory manufactured from vegetable oils.
What Is Potassium Azeloyl Diglycinate? The Anti-Inflammatory Ingredient to soothe Rosacea, a Damaged Skin Barrier & Sensitive Skin
PAD is a water-soluble AzA derivative, and one of QR8’s newest ingredients. It is produced by reacting azelaic acid with 2 molecules of glycine and potassium hydroxide.
It has a few advantages over traditional AzA including better moisturising capability due to the addition of glycine, improved solubility (because azelaic acid alone has very poor solubility, and often forms crystals in formulations) and tolerability, whilst providing the same benefits that AzA does in the treatment of a multitude of skin disorders.
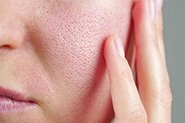
What can AzA and PAD treat?
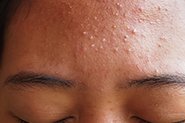
AzA and PAD have a role in the treatment of mild-moderate acne vulgaris (and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation), rosacea, and melasma
Are Azelaic Acid and Potassium Azeloyl Diglycinate Effective Topical Treatments for Acne?
AzA has selective antimicrobial activity against the bacteria that are most often associated with acne – Cutibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis. This means it can reduce the numbers of these without harming other skin bacteria in the skin microbiome.
In several studies, AzA is as effective as 5% benzoyl peroxide as an acne treatment, without the burning/irritation (and towel bleaching!). Aza is also as effective as topical antibiotics often used in dermatologist-recommended acne treatments such as 1% clindamycin and 2% erythromycin.
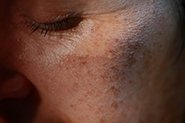
Together with its anti-inflammatory activity and ability to unblock comedones (blackheads/whiteheads) it can help reduce lesion counts in mild-moderate acne vulgaris. Azelaic Acid is also effective in fading dark spots left behind from acne lesions (‘post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation’ or PIH).
There is minimal data for the effect of PAD in acne – as a derivative of AzA, it may well also have some antimicrobial activity. At the time of writing, AzA is the preferred ingredient in Qr8 personalised acne skincare formulations due to strong evidence supporting its effectiveness in acne management, and helping to fade acne scars (PIH).
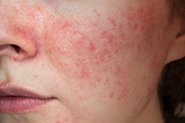
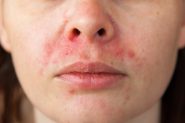
Are Azelaic Acid and Potassium Azeloyl Diglycinate The Best Rosacea Treatments?
There is high quality evidence from multiple clinical trials that AzA can reduce inflammation/redness and inflammatory lesions like the papules and pustules of rosacea.
Some studies have suggested that certain inflammatory chemicals in the skin (such as cathelicidin and kallikrein 5) have a role in rosacea, and AzA has been shown to reduce these.
Potassium Azeloyl Diglycinate has demonstrated good effect on multiple aspects of rosacea, including improving redness and inflammation as part of a rosacea skincare routine. It can also help reduce superficial broken blood vessels. PAD has also demonstrated better tolerability, and causes less stinging and burning skin in rosacea patients than other commonly used treatments (including AzA and metronidazole), making it suitable to soothe sensitive skin.
Because of their role in treating rosacea, both azelaic acid and PAD are available for our doctors to include in Qr8 rosacea treatments, along with multiple other evidence-based ingredients that treat rosacea.
Azelaic Acid hasn’t shown much effect on reducing the appearance of broken blood vessels (known medically as telangiectasia).
Read more about Oxymetazoline another of our science-backed ingredients that reduces facial redness HERE >>
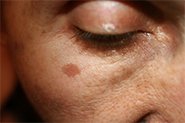
Can Azelaic Acid and Potassium Azeloyl Diglycinate Treat Melasma?
AzA inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase which is required by the cells that produce melanin in our skin (melanocytes) – it’s this melanin that shows up as dark blotches on our skin with melasma. There is also evidence that it can reduce the numbers of hyperactive melanocytes in people with melasma.
PAD has also demonstrated effectiveness in the treatment of melasma and improving the appearance in mild to moderate cases… it goes without saying, but the effectiveness of these ingredients in treating hyperpigmentation also depends on the gold-standard of melasma treatment (the right kind of tinted sunscreen!) being used. Read more about that HERE >>
What’s the scientifically-backed dose of Azelaic Acid and PAD for their effectiveness?
You’ll find 10% Azelaic Acid in cosmetic products everywhere, but what’s the effective dose of Azelaic Acid?
It might surprise you to know that scientific studies show 15-20% AzA is used for conditions like acne and rosacea, and typically needs to be applied twice daily unless combined with other prescription ingredients. So your 10% cosmetic dose might do something (but it also might do nothing at all!).
It is also safe to use Azelaic Acid for patients who are trying to conceive, pregnant and breastfeeding and wanting to manage their hormonal pigmentation, rosacea and pregnancy acne.
PAD is used cosmetically anywhere from 0.5-3%. At Qr8 we use 5% PAD in our formulations, as studies have shown that formulations containing 5% PAD deliver comparable results to those with 15% Azelaic Acid.
You may see cosmetics with wild claims about 10% PAD in their formulations - this is very likely not true.
This is marketing wording that actually means a formula contains '10% PAD solution' - except that the original PAD solution is not at 100% concentration. One fabulous company realised their mistake and went public about it - but sadly not everyone is this honest. Click my headshot below to read more their explanation (and bravo to them for their honesty!)
How Long Before I See Results Using Azelaic Acid and PAD?
This will vary patient-to-patient, and depends on a number of factors, including what condition is being treated, its severity and if you are following advice on your supporting skincare (including… you’ve guessed it… your sunscreen!).
What are the Side Effects of Azelaic Acid & PAD?
Azelaic Acid is normally very well tolerated – some people experience mild and localised stinging, burning or itching when they first start using AzA, especially when used with strong night treatments, so our Qr8 Support Team will always help you phase it in carefully to get the best results. This is because with inflammatory skin diseases like acne, rosacea and melasma, side effects will increase inflammation and can make your skin condition worsen. That’s just one of the reasons our patients see such great results with our world-first Qr8 Code (read more about why it’s unique HERE >>)
As mentioned, PAD has shown even greater tolerability than AzA, but some patients may still occasionally get the side effects outlined above, especially if it was included at dosages like 10%!!
WE SEE YOU. WE UNDERSTAND YOUR FRUSTRATION WITH FINDING SOLUTIONS FOR MELASMA, ACNE, SUN DAMAGE, ROSACEA AND PIGMENTATION.
WE’RE HERE TO HELP.
BOOK A CONSULTATION WITH AN EXPERIENCED AUSTRALIAN DOCTOR TODAY TO DISCUSS YOUR SKIN TREATMENT OPTIONS: CLICK HERE
REFERENCES:
Schulte BC, Wu W, Rosen T. Azelaic Acid: Evidence-based Update on Mechanism of Action and Clinical Application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015 Sep;14(9):964-8. PMID: 26355614
Berardesca E, Iorizzo M, Abril E, Guglielmini G, Caserini M, Palmieri R, PiérardGE. Clinical and instrumental assessment of the effects of a new product basedon hydroxypropyl chitosan and potassium azeloyl diglycinate in themanagement of rosacea. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012 Mar;11(1):37-41. PMID:22360333.
4.Veraldi S, Raia DD, Schianchi R, De Micheli P, Barbareschi M. Treatment ofsymptoms of erythemato-telangiectatic rosacea with topical potassium azeloyldiglycinate and hydroxypropyl chitosan: Results of a sponsor-free, multicenter,open study. J DermatologTreat. 2015 Apr;26(2):191-2. PMID: 24831156.
Celleno L, Bussoletti C, CaseriniM, Palmieri R. Instrumental assessment of the soothing effect of a new product based on hydroxypropyl chitosan andpotassium azeloyl diglycinate. J Plast Dermatol. 2012;8:33–5.3
5.Viyoch J, Tengamnuay I, Phetdee K, Tuntijarukorn P, Waranuch N. Effects oftrans-4-(aminomethyl) cyclohexanecarboxylic acid/potassium azeloyldiglycinate/niacinamide topical emulsion in Thai adults with melasma: a single-center, randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp.2010 Dec;71(6):345-59. PMID: 24688154.