What is Azelaic Acid?
Azelaic acid (AzA) is one of our favourite ingredients at Qr8 Mediskin. You will find it in our acne, rosacea, and daytime fading treatments. It is safe to use in pregnancy, and for long-term use, so forms the cornerstone of our maintenance products.
AzA (chemical name: 1,7-heptanedicarboxylic acid) is a naturally-occurring dicarboxylic acid. Although it is found naturally in barley, wheat, and rye, it isn’t sustainable to produce Aza commercially from grains. Skincare-grade AzA is lab-manufactured from oleic acid obtained from vegetable oils.
What can Azelaic Acid treat?
AzA is a workhorse ingredient when used within its effective concentration range ! It is used to treat mild-moderate acne vulgaris (and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation), rosacea, and melasma. In mild cases, AzA can be used as the primary treatment, but it is most often used as an additional (‘adjunctive’) treatment with other prescription actives to superpower results
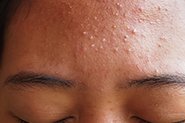
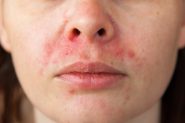
Acne
AzA has selective antimicrobial activity against Cutibacterium acnes (the new name for Propionibacterium acnes) and Staphylococcus epidermidis, meaning it can reduce the numbers of these without harming other skin bacteria. In several studies, AzA is as effective as 5% benzoyl peroxide, without the burning/irritation (and towel bleaching!), and topical antibiotics such as 1% clindamycin and 2% erythromycin. Together with its anti-inflammatory activity and ability to unblock comedones (blackheads/whiteheads) it can help reduce lesion counts in mild-moderate acne vulgaris.
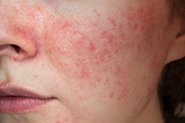
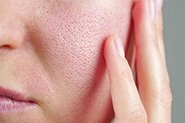
Rosacea
How AzA works to reduce rosacea symptoms isn’t yet clear, although there is high quality evidence from multiple clinical trials that it can reduce inflammation/redness and inflammatory lesions (not those pesky broken vessels though). Some studies show that it can reduce inflammation triggers in the skin like cathelicidin and kallikrein 5.
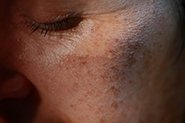
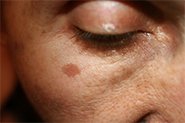
Melasma
AzA inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase which is required by melanocytes to produce the melanin pigments that show up as dark blotches on our skin. There is also evidence that it can reduce the numbers of abnormal melanocytes.
How long before I see results?
You may see initial improvement within 1 month, but at least 2-3 months of treatment are usually required to see a significant improvement.
Any side effects?
AzA is normally very well tolerated – certainly way more than retinoids initially! Some people experience very mild and localised stinging, burning or itching when they first start using AzA, so we help you phase it in quickly but carefully to get the best results. Any minor irritation usually resolves with continued use – in one study of 333 patients, less than 1 percent of all patients had persistent sensory symptoms.
Want to get started? Click here >
REFERENCES
Schulte BC, Wu W, Rosen T. Azelaic Acid: Evidence-based Update on Mechanism of Action and Clinical Application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015 Sep;14(9):964-8. PMID: 26355614.